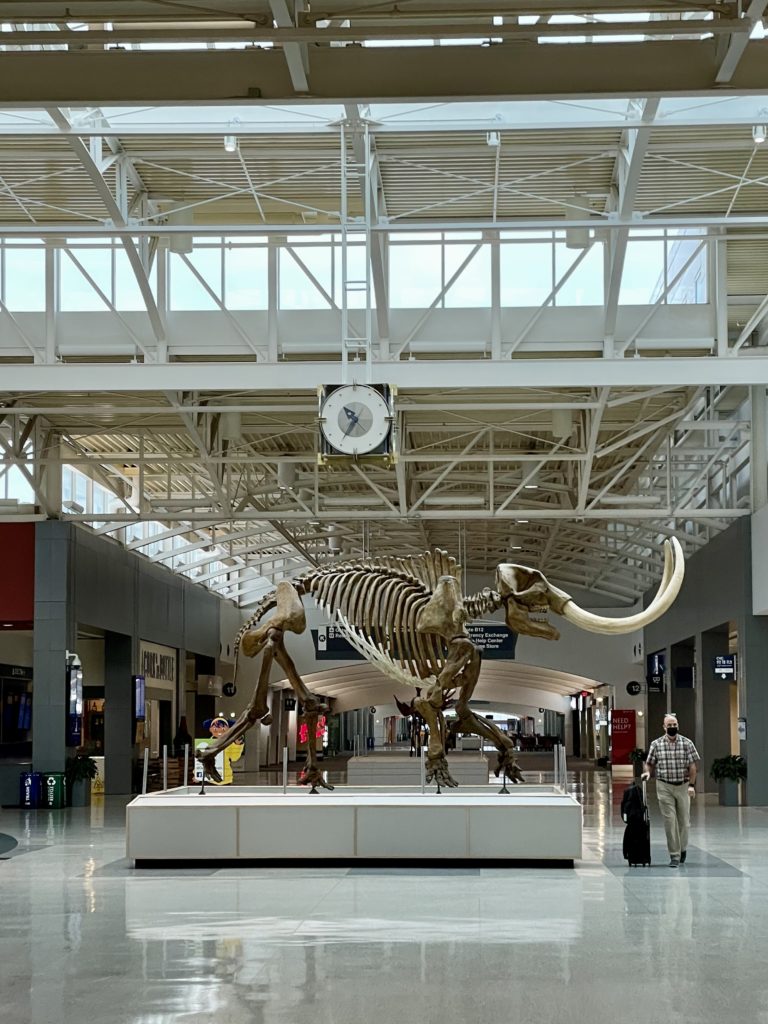
Megafauna skeletons on display at the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport (CVG), just south of the Ohio River in Boone County, Kentucky). The famous paleontological site, Big Bone Lick, is only about 20 miles south of the airport.



You begin to interest me…vaguely
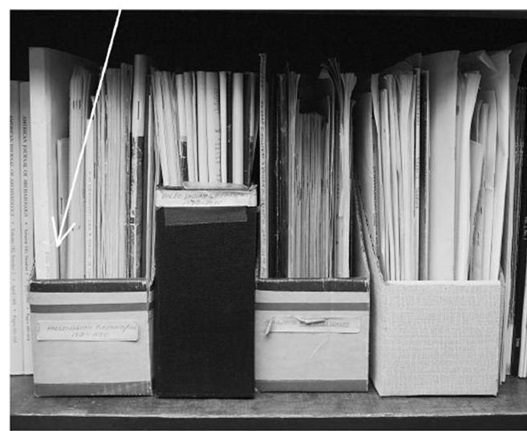
Before eminent archaeologist John Cotter passed away in 1999, he donated much of his personal library to his colleague Anthony Boldurian and the University of Pittsburgh at Greensburg. As they sorted through the books, file folders, and papers, they found something completely unexpected: a plastic sandwich bag with two neatly wrapped Clovis fluted points inside.

Cotter is best known as one of the pioneers of American historical archaeology, but he began his career studying Paleoindian archaeology, earning his M.A. in 1935. He had originally planned to write his dissertation on the Clovis material from Blackwater Draw, but by the time he returned to graduate studies at Penn in the 1950s, he had switched his subject to the excavations he had done at historic Jamestown, Virginia with the National Park Service. Yet he always maintained an interest in Paleoindian archaeology, and in fact his final publication, with Boldurian, was titled Clovis Revisited.
One of the points was labeled with his name and the location “Western Kentucky 1939.” At that time, Cotter was the state supervisor of the Archaeological Survey of Kentucky, and much of his time was spent examining the multiple excavations underway and ferrying supplies and artifacts to and from the laboratory, but there is no other contextual information for this point.
The second point is unlabeled, but made from a type of chert (Vera Cruz jasper) found in eastern Pennsylvania. The authors don’t say how difficult it was to figure this one out, but they matched this point to a photo of a fluted point found in New Jersey and published in one of the early articles on Paleoindian stone tools, Edgar B. Howard’s 1934 “Grooved Spearpoints.” That New Jersey point was in the collections of the University Museum at the University of Pennsylvania, where Cotter became a professor and curator. The authors found a drawing of the same Clovis point in the appendix of Cotter’s 1935 thesis.
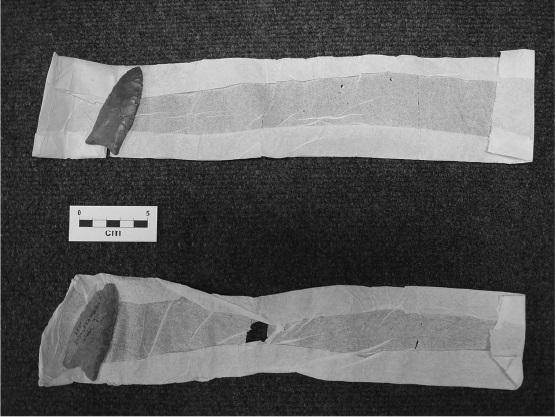
The projectile point is part of the Newbold collection, accumulated by a New Jersey gentleman farmer in the second half of the nineteenth century. Michael Newbold would pay his workers as much as five cents for artifacts they found on his farm in Burlington County. After his death, the then-new University Museum acquired his collection – decades before anyone knew how old those fluted points were.
How did they end up among the paperwork? It seems likely Cotter was working with the specimens (he was particularly interested in a specific diagnostic characteristic, called basal polish or basal edge grinding, that both points have) in his office and at some point –perhaps even after his death– the bag holding them got bundled up with related articles and filed away in a bookshelf. It’s a nice example of lost artifacts being found again.

Reference:
Boldurian, Anthony T., Justin D. McKeel, and Mason G. Pickel
2012 Gifts from an archaeologist’s bookcase: John L. Cotter’s library. North American Archaeologist 33(2):193-237.